S+S control technology
Installation in switchgear
S+S control technology
S+S control technology
S+S control technology
VFTF-U 0...100%, TT adjustable, 2x 0-10V, ±2%, Vitrin-TT / RH sensor, active outputs
Condensation & Dew Point Sensors
Condensation & Dew Point Sensors
S+S control technology
KFTF-20-I 4...20mA Channel sensor RH/temperature active ±1, 8% accurate, Pleuroform, TYR I
Screw-in & Channel Sensors
KFTF-20-I VA 4...20mA, ±1, 8%, stainless steel housing, channel sensor TT / RV
S+S control technology
KFTF-20-U 0-10V Channel sensor RH/temperature active ±1, 8% accurate, Pleuroform, TYR I
S+S control technology
KFTF-U, NTC 1, 8K Channel humidity and temperature sensor, Pleuroform, TYR I
Condensation & Dew Point Sensors
KW-W-SD external changeover contact, IP43, Condensation monitor
separate moisture sensor
MSK-25 measuring head (RH sensor), pluggable, for moisture AFF-25 / AFTF-25
Hygrostats
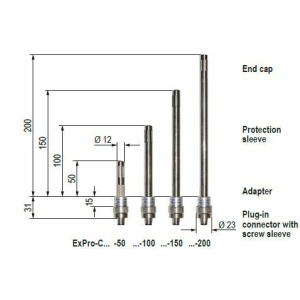
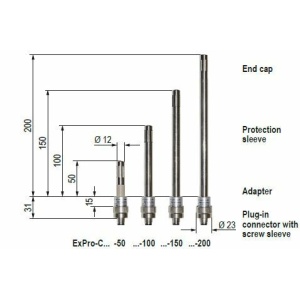
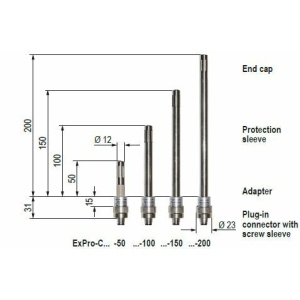
Explosion-proof
Explosion-proof
Explosion-proof
Explosion-proof
Explosion-proof
S+S control technology
RFF-I Display 4...20mA, 0...100% r.H. (± 3%), Room moisture sensor (surface mount) BALDUR I
S+S control technology
RFF-I Display 4...20mA, 0...100% r.H. (± 3%), Room moisture sensor (surface mount) BALDUR II
Müller IE
Air quality sensors CO2
RFTM-CO2-Modbus CO2 0...5000ppm, Rv: 0...100%, TT 0...50°C Modbus-RTU, BALDUR II
Condensation & Dew Point Sensors
TW-Modbus Tube 0...100% rH, Dew point sensor with Modbus RTU, incl. Y adapter
Condensation & Dew Point Sensors
TW-Modbus-External 0...100% rH, Dew point sensor with Modbus RTU, incl. Y adapter
Condensation & Dew Point Sensors
TW-Modbus-External Display 0...100% rH, Dew point sensor with Modbus RTU, incl. Y adapter
Condensation & Dew Point Sensors
TW-U / W-tube 0...100% rH, 0-10V + Changeover contact Dew-point sensor
Condensation & Dew Point Sensors
Condensation & Dew Point Sensors
TW-W-External Display 75...100% rH, Changeover contact Dewpoint sensor
S+S control technology
VFF-I 0...100%, 4...20mA, ±2%, Vitrin moisture sensor with active output
S+S control technology
VFF-I Display 0...100%, 4...20mA, ±2%, Vitrin moisture sensor with active output
S+S control technology
VFF-U 0...100%, 0-10V, ±2%, Vitrin moisture sensor with active output
S+S control technology
VFF-U Display 0...100%, 0-10V, ±2%, Vitrin moisture sensor with active output
S+S control technology
VFTF-U 0...100%, TT adjustable, 2x 0-10V, ±2%, Vitrin-TT / RH sensor, active outputs
Explosion-proof
Explosion-proof
Explosion-proof
Explosion-proof temperature and humidity sensor ExCos-D series
Moisture sensors
Operation of Moisture Sensors: The basics of moisture sensors vary, but most use one of the following techniques:Capacitive Sensors: Capacitive humidity sensors measure humidity by the change in capacitance of a capacitor. A thin polymer film, sensitive to moisture, acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. When humidity increases, the polymer film absorbs water, changing the capacitance of the capacitor. This change is converted into an electrical signal proportional to humidity.
Resistance sensors: Resistance sensors measure humidity by recording the resistance of a hygroscopic material. This material absorbs moisture from the environment, leading to a change in electrical resistance. This change is measured and converted into a humidity level.
Optical Sensors: Optical humidity sensors use the absorption and reflection properties of water vapor in the air. By measuring changes in light intensity or wavelength, these sensors can accurately determine humidity levels.
Resistive Sensors: Resistive humidity sensors have a hygroscopic material that affects electrical resistance based on humidity. Changes in resistance are measured and translated into a humidity reading.
Applications of Moisture Sensors: The versatility of moisture sensors makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
Climate control systems in buildings - Industrial processes where accurate humidity control is essential - Agriculture, for soil moisture monitoring - Medical applications, such as respiratory monitoring in medical devices. Consumer electronics, such as humidity sensors in weather stations and smart thermostats.